Enhancing Kubernetes Management with ChatOps: Integrating Claude Desktop and K8SGPT MCP
When you type into a chat:
“Analyze my Kubernetes cluster”
“What's the health status of my cluster?”
“Show me any issues in the default namespace”
These are not just dry commands—they are a call for a revolution in how we manage infrastructure. Instead of jumping between terminals, dashboards, and countless documents, you can now use natural language to instantly gain a comprehensive view of your Kubernetes cluster’s status, performance, and issues. With ChatOps, every interaction becomes intuitive, every issue is detected quickly, and every remedial action can be executed immediately—all within a single chat interface.
What is ChatOps?
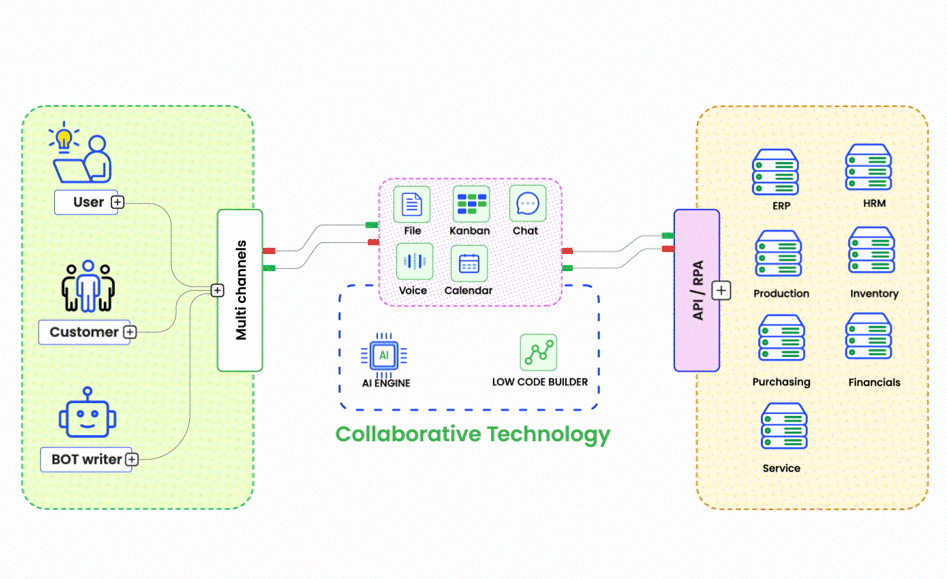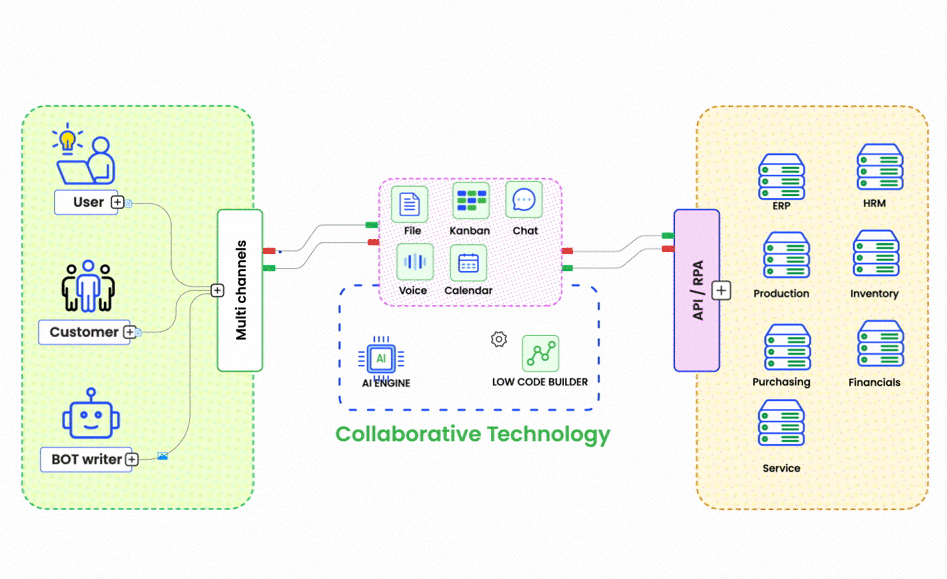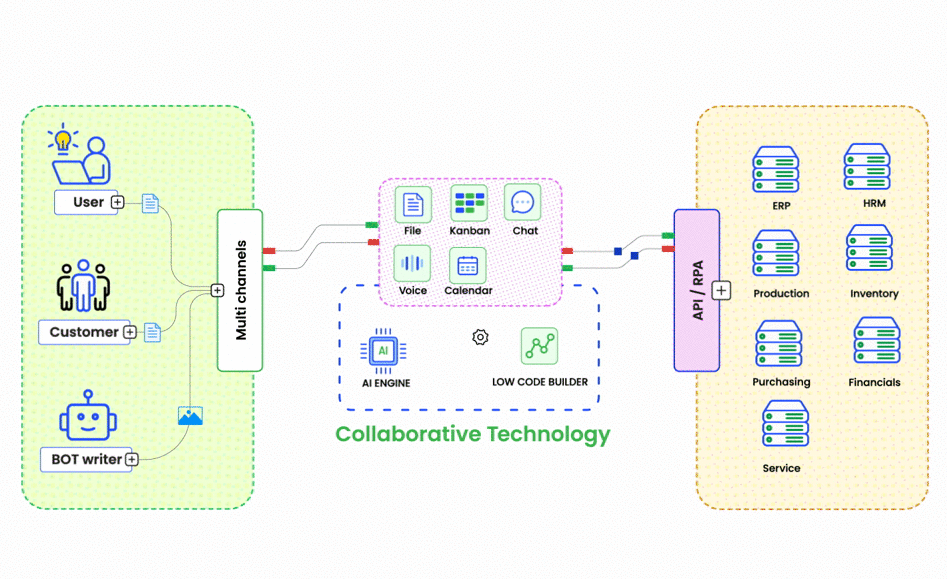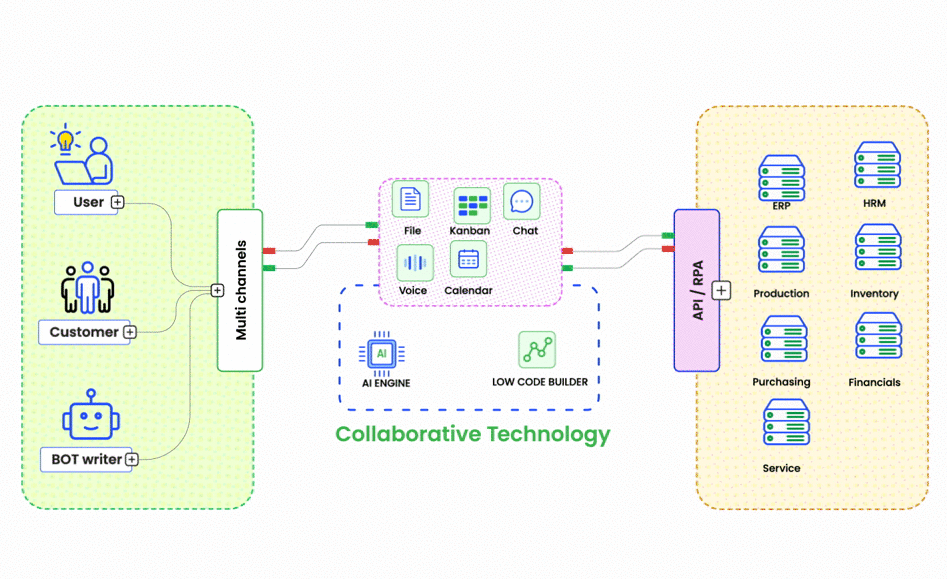
ChatOps is a collaborative model that integrates chat tools with automation and monitoring systems, enabling teams to execute commands, trigger workflows, and monitor systems directly from chat applications like Slack or Microsoft Teams. This approach offers several benefits:
- Automation: Reduces human error by automating repetitive tasks.
- Transparency: All actions are logged in the chat history, providing real-time visibility.
- Collaboration: Team members can discuss and act on the same platform, improving communication.
- Compliance: Chat history provides an audit log for regulatory compliance efforts.
For example, a team might use a command like !deploy to deploy code or check the status of a Kubernetes cluster, with results displayed directly in the chat channel (ChatOps Definition).
Introducing Claude Desktop
Claude Desktop is a desktop application developed by Anthropic, bringing the capabilities of the Claude AI model directly to users’ computers. Unlike the web version, Claude Desktop is designed to integrate seamlessly with local workflows, offering features such as:
- Natural Language Processing: Claude can understand and respond to complex queries, making it suitable for conversational interactions.
- Code Generation: Supports writing and debugging code, useful for DevOps developers.
- MCP Integration: Through the Model Context Protocol (MCP), Claude Desktop can connect to external tools, such as file systems or services like K8sGPT (Claude Desktop).
MCP is a standard that enables AI applications like Claude Desktop to interact securely with external data sources or tools, such as code repositories or Kubernetes clusters. This makes Claude Desktop an ideal platform for ChatOps applications, where automation and real-time interaction are critical (Model Context Protocol).
Exploring K8SGPT

K8SGPT is an innovative tool designed to simplify Kubernetes cluster management using artificial intelligence. It acts as an intelligent assistant, providing the following capabilities:
- Cluster Analysis: K8sGPT uses analyzers to inspect Kubernetes components like pods, services, and deployments, identifying potential issues.
- Troubleshooting: It provides detailed fix suggestions, often accompanied by easy-to-understand explanations.
- Customization: Users can write custom analyzers to meet the specific needs of their clusters.
- AI Integration: K8sGPT leverages large language models to deliver human-like responses, making it accessible to non-experts (K8sGPT GitHub).
For example, K8sGPT can detect a failed pod in the default namespace and suggest remediation steps, such as checking logs or adjusting resource limits. When integrated with Claude Desktop, these interactions can be performed via natural language commands, enhancing the ChatOps experience.
Integrating K8SGPT with Claude Desktop
Integrating K8sGPT with Claude Desktop enables users to manage Kubernetes clusters through natural language queries within the Claude Desktop interface. The setup process involves the following steps:
- Install K8SGPT: Install K8SGPT following the official GitHub instructions, for example, using Homebrew with the command brew install k8sgpt (K8sGPT GitHub).
- Install Claude Desktop: Download and install Claude Desktop from Anthropic’s website (Claude Desktop).
- Use Natural Language Commands: Once set up, users can input queries like “Analyze my Kubernetes cluster” or “Show issues in the default namespace” to receive insights and recommendations from K8sGPT.
- Configure Claude Desktop: In Claude Desktop, navigate to Settings > Integrations, and add K8sGPT. The MCP server is typically detected automatically.
# Example configuration
{
"mcpServers": {
"k8sgpt": {
"command": "C:\\Users\\ADMIN\\Downloads\\k8sgpt_Windows_x86_64\\k8sgpt.exe",
"args": [
"serve",
"--mcp",
"--kubeconfig", "C:\\Users\\ADMIN\\Downloads\\k8sgpt_Windows_x86_64\\platform-tooling.kubeconfig"
]
}
}
}- Restart Claude Desktop: After you set up sucessfully, you can see the config like this in Claude Desktop:
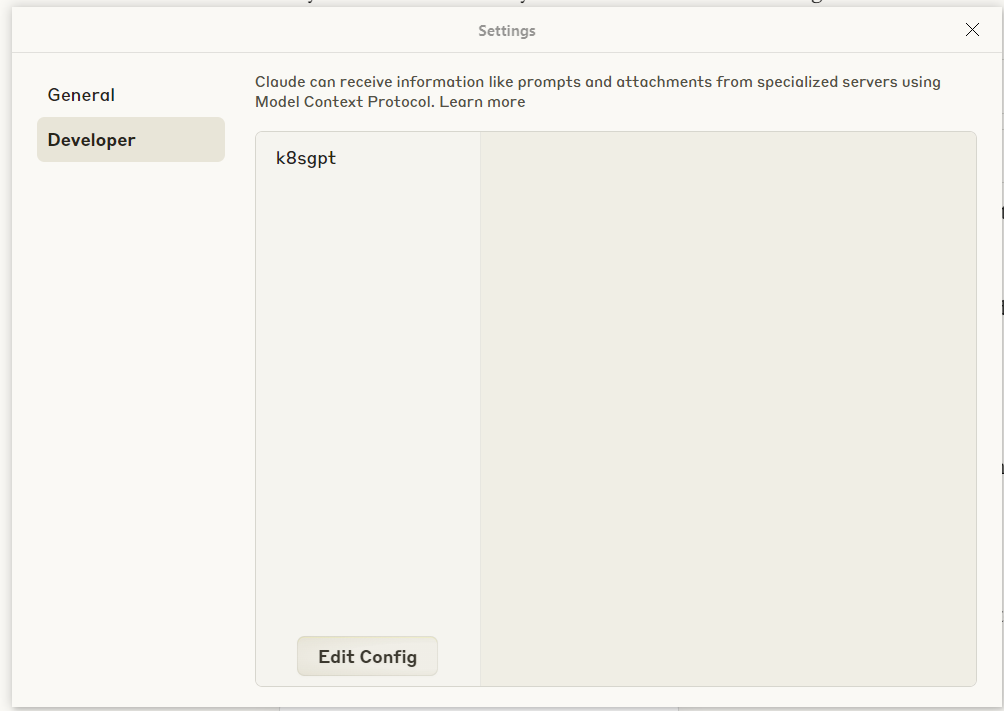
Then, enjoy it! Below is my example:
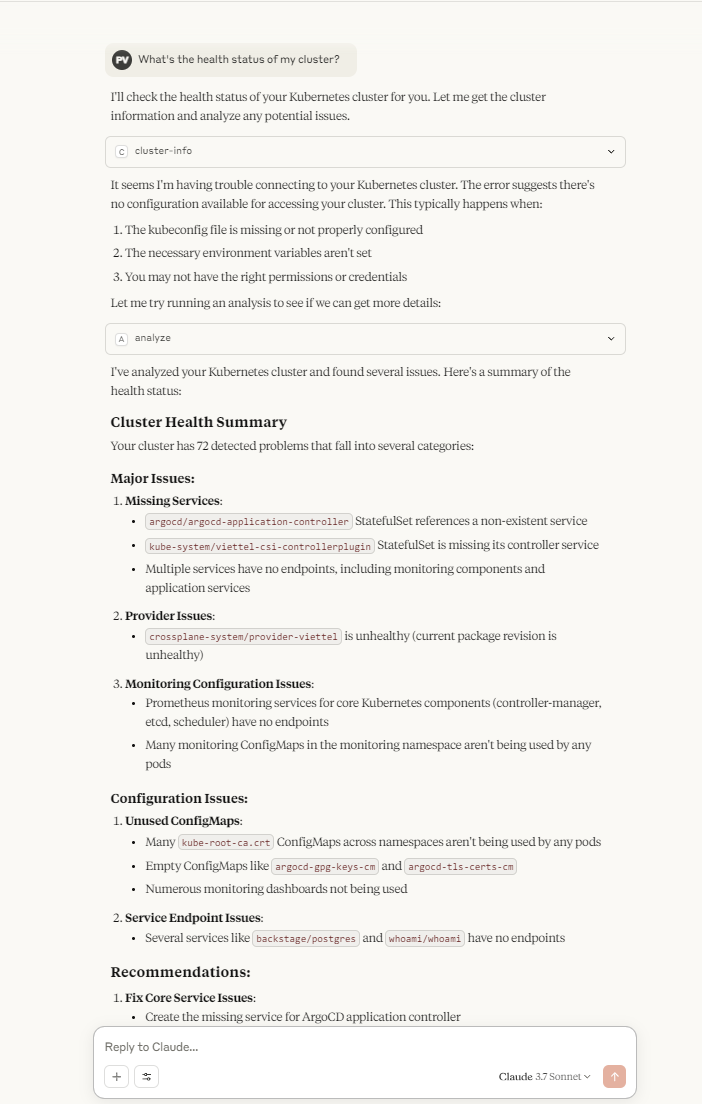
Note: This integration requires K8sGPT version 0.4.14 or higher. Users must also ensure their Kubernetes cluster is accessible and the MCP server is running without errors.
Example Commands
Below are some sample commands users can use in Claude Desktop after integration:
Command | Result |
|---|---|
Analyze my Kubernetes cluster | K8sGPT runs analyzers and returns a report on the cluster’s status, including any detected issues. |
What is the status of pods in the default namespace? | Displays a list of pods in the default namespace along with their status and any errors. |
Suggest how to fix a stuck pod | K8sGPT provides remediation steps, such as checking logs or adjusting configurations. |
Troubleshooting
If the integration does not work, check the following:
- Is the MCP server running (k8sgpt serve --mcp)?
- Is the Kubernetes cluster accessible from your environment?
- Are both Claude Desktop and K8sGPT updated to the latest versions?
Use Cases
- Pod Troubleshooting: A developer notices an unresponsive application and uses Claude Desktop to request K8sGPT to analyze related pods, receiving immediate fix suggestions.
- Cluster Monitoring: A DevOps team sets up recurring commands to check cluster health, with reports sent directly to their chat channel.
- Configuration Generation: K8sGPT can assist in creating Kubernetes YAML files based on natural language descriptions, such as “Create a deployment with 3 replicas.”
Future Development Directions
Beyond integrating K8SGPT into ChatOps, there are exciting opportunities to expand the ChatOps ecosystem by incorporating additional tools via the Model Context Protocol (MCP). These integrations can further enhance DevOps workflows by providing a unified interface for monitoring, automation, and CI/CD operations like: Grafana, Jenkins, Loki, AWS, etc.
Conclusion
The combination of Claude Desktop and K8SGPT represents a significant step forward in applying ChatOps to Kubernetes management. By leveraging Claude Desktop’s intuitive chat interface and K8SGPT’s AI-driven analysis, DevOps teams can manage Kubernetes clusters more efficiently, transparently, and collaboratively. While the setup may require some technical effort, the benefits in productivity and accessibility make this integration an attractive choice for organizations looking to simplify their Kubernetes operations.