Exploring Telco Cloud: The Cloud Shaping the Future of Telecommunications
Telco Cloud, or telecommunications cloud, is becoming one of the most important technologies in the modern telecommunications industry. It enables telecommunications service providers (telcos) to transform traditional network infrastructure into a more flexible, efficient, and scalable system. With the development of 5G and future technologies, Telco Cloud plays a crucial role in deploying new networks and providing advanced services. In this article, we will explore what Telco Cloud is, its benefits, how it works, recent trends, and its importance in the current context.
What is Telco Cloud?
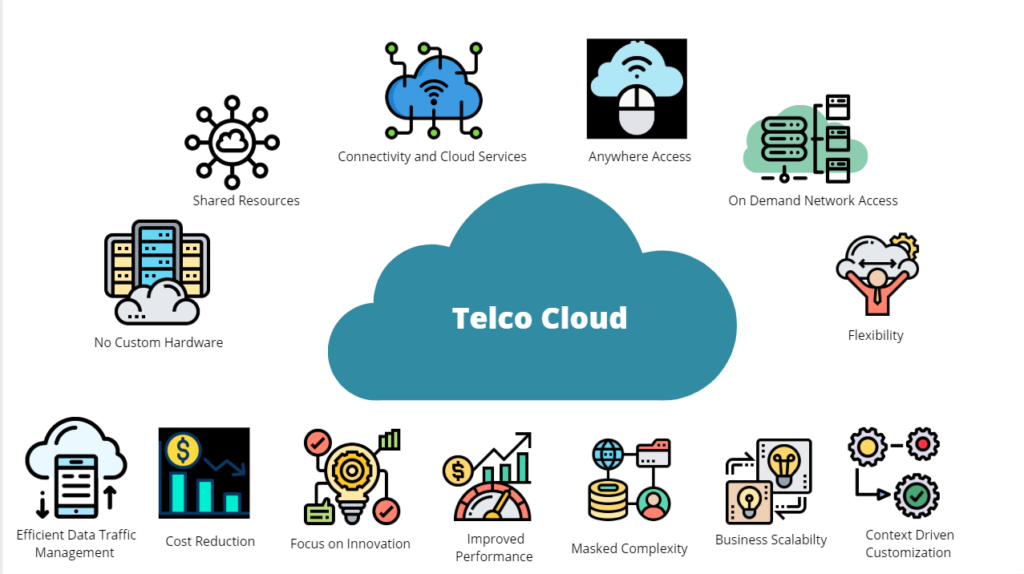
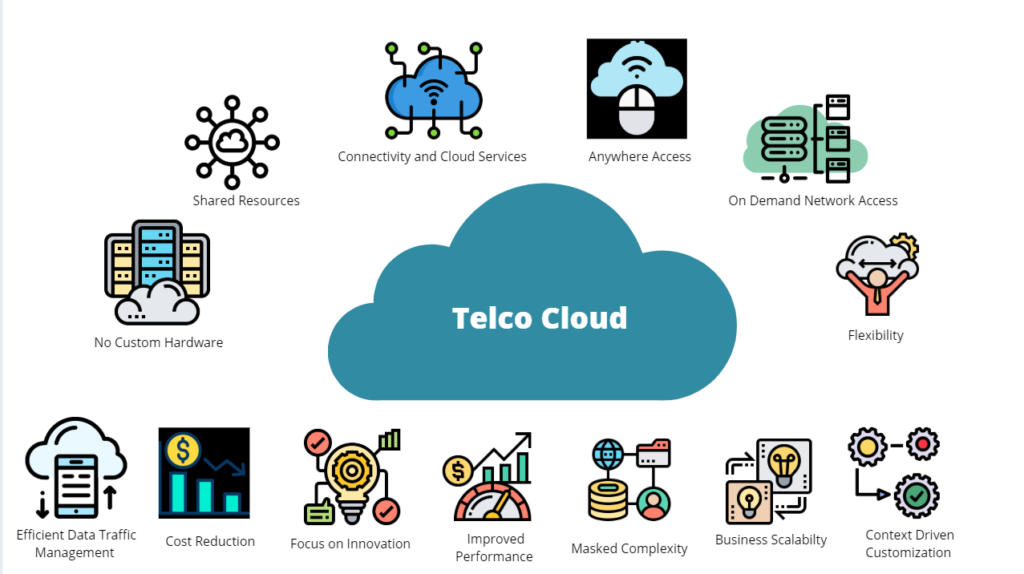
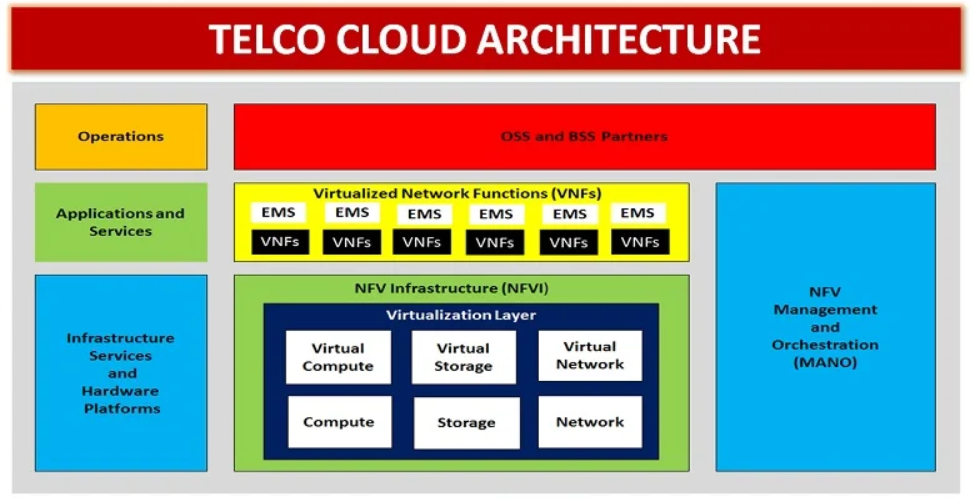
Telco Cloud is a software-based cloud infrastructure specifically designed for telecommunications service providers. It allows telcos to virtualize and manage network functions, enabling them to quickly add new services, respond faster to changes in network demand, and manage resources more efficiently. Telco Cloud is a key component in the digital transformation of telecommunications companies, helping them become digital service providers.

Unlike traditional clouds, Telco Cloud is optimized to meet the stringent requirements of the telecommunications industry, such as high reliability (99.999% uptime, equivalent to 5.26 minutes of downtime per year) and low latency. It combines technologies like network function virtualization (NFV), containers, microservices, and hybrid cloud architecture to support complex network applications.
The Development of Telco Cloud
Telco Cloud began with the concept of network function virtualization (NFV), where traditional network functions, such as routing or firewalls, were moved from dedicated hardware to software running on commodity hardware. This helped reduce costs and increase flexibility. With the advent of 5G, Telco Cloud has expanded to include new technologies like containers, microservices, and hybrid cloud architecture.

Today, Telco Cloud not only focuses on virtualization but also on cloud-native network functions (CNF - Cloud-Native Network Functions). CNF breaks down network functions into smaller microservices running in containers, enhancing efficiency and scalability. The transition from NFV to CNF marks a significant step forward, allowing telcos to deploy networks faster and leverage public cloud platforms to reduce costs.
Benefits of Telco Cloud
Telco Cloud brings several important benefits to telcos, including:
- Enhancing business agility: Telco Cloud enables telcos to quickly deploy new services, such as IoT applications or enterprise services, to meet market demands.
- Cost reduction: By using commodity hardware and automation, Telco Cloud helps reduce capital expenditures (CapEx) and operational expenditures (OpEx).
- New service opportunities: It opens up new revenue streams from 5G, such as network slicing or edge computing applications, while strengthening digital customer relationships through data analytics and AI.
- Better network management: Telco Cloud allows for efficient management of centralized and decentralized resources, ensuring optimal network performance.
How Does Telco Cloud Work?
Telco Cloud works by virtualizing traditional network functions, allowing them to run on commodity hardware instead of dedicated hardware. It uses technologies like containers and microservices to create more flexible and scalable network functions. For example, a network function like packet switching can be broken down into multiple microservices, each running in its own container.
Telco Cloud also supports hybrid and multi-cloud architectures. High-performance network functions, such as the 5G core, can be deployed on private clouds to ensure reliability. Meanwhile, less critical functions, such as business support systems (BSS), can run on public clouds to reduce costs.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Software-based cloud infrastructure for telcos, supporting virtualization and efficient network function management. |
| Key Technologies | NFV, containers, microservices, hybrid cloud architecture. |
| Deployment | Combines private cloud (for high performance) and public cloud (for low cost). |
| Performance Requirements | 99.999% reliability (5.26 minutes of downtime per year), low latency. |
| Applications | Supports 5G, IoT, edge computing, and digital services. |
Recent Trends in Telco Cloud
The telecommunications industry is witnessing several new developments related to Telco Cloud:
- 5G Core Deployment: Telcos are transitioning from 5G Non-Standalone (NSA) to Standalone (SA) cores, with SA cores being fully cloud-native, supporting features like network slicing and low-latency communications (Telco Cloud Deployment Tracker - STL Partners).
- vRAN and Open RAN: Virtualized Radio Access Networks (vRAN) and Open RAN are being widely deployed, with major telcos like AT&T, Deutsche Telekom, and Vodafone leading the way. These technologies enhance openness and reduce vendor lock-in (Telco cloud: Where are we at in 2024? - STL Partners).
- Market Growth: The Telco Cloud market is expected to reach $27 billion by 2027, driven by the shift to CNF and container-as-a-service (CaaS) platforms (Telco Cloud Infrastructure Software Market - IDC).
- Cloud-Native Transformation: Telcos are moving from VNF to CNF, leveraging Kubernetes and container platforms to increase efficiency.
- Collaboration and Innovation: Companies like Ericsson and Google Cloud are collaborating to develop cloud-native 5G core solutions, such as Ericsson deploying CNF on Google Distributed Cloud Edge (The Telco Cloud-Native, 5G-Core Revolution - Telecom Review).
Case Studies and Examples
Telco Cloud has been successfully adopted by many telecommunications companies worldwide:
- Rakuten Mobile: Rakuten built the first fully cloud-based 5G network, using Telco Cloud to reduce costs and accelerate deployment. This network supports the growing demand for mobile users and remote work (Telco Cloud - Cisco).
- T-Systems: T-Systems used Telco Cloud to simplify and secure its cloud infrastructure, combining the benefits of private and public clouds to provide flexibility and security.
- Vodafone: Vodafone partnered with Google Cloud to use AI, reducing the number of operational tools by half, thereby increasing efficiency and reducing costs (Cloud Telecom Solutions | Google Cloud).
- Turkcell: Turkey's leading telco separated its digital services into independent platforms, such as messaging, entertainment, and cloud services, generating $150 million in revenue in 2021, accounting for 8% of total revenue (The future of telcos - McKinsey).
The Future of Telco Cloud
Telco Cloud continues to evolve with the emergence of new technologies such as edge computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and automation. It will play a crucial role in deploying 5G and future network generations, enabling telcos to provide low-latency and high-speed services. Additionally, Telco Cloud will help telcos transition from connectivity providers to comprehensive digital service providers, offering digital solutions to businesses and consumers.
In the future, we can expect:
- The rise of edge computing applications to support services like autonomous vehicles and virtual reality.
- Deeper integration with AI to optimize network management and customer experience.
- Expansion of Open RAN platforms, helping to reduce costs and increase competitiveness.
Conclusion
Telco Cloud represents a significant advancement in the telecommunications industry, allowing telcos to transform traditional network infrastructure into a flexible, efficient, and scalable system. With benefits in cost, flexibility, and scalability, Telco Cloud is not just a trend but a necessary element for the future development of the telecommunications industry. As 5G and new technologies continue to shape the world, Telco Cloud will be the foundation that helps telcos compete and thrive in the digital era.